- change the scene;
- compress time;
- vary the point of view; or
- build up an image or idea.
- continuity of direction;
- completed action;*
- a similar centre of attention in the frame;
- a one-step change of shot size (e.g. long to medium);
- a change of angle (conventionally at least 30 degrees).
- introduce particular parts of a programme;
- to add extra information not evident from the picture;
- to interpret the images for the audience from a particular point of view;
- to link parts of a sequence or programme together.
- the use of matched cuts (rather than jump cuts);
- motivated cuts;
- changes of shot through camera movement;
- long takes;
- the use of the sound bridge;
- parallel development.
- Arijon, Daniel (1976): Grammar of the Film Language. London: Focal Press
- Bordwell, David & Kristin Thompson (1993): Film Art: An Introduction. New York: McGraw Hill
- Izod, John (1984): Reading the Screen (York Handbooks). Harlow: Longman
- Millerson, Gerald (1985): The Technique of Television Production. London: Focal Press
- Monaco, James (1981): How to Read a Film. New York: Oxford University Press
- Sobchack, Thomas and Vivian C Sobchack (1980): An Introduction to Film. Boston: Little, Brown and Company
- Watts, Harris (1984): On Camera. London: BBC
The 'Grammar' of Television and Film
Television and film use certain common conventions often referred to as the 'grammar' of these audiovisual media. This list includes some of the most important conventions for conveying meaning through particular camera and editing techniques (as well as some of the specialised vocabulary of film production).Conventions aren't rules: expert practitioners break them for deliberate effect, which is one of the rare occasions that we become aware of what the convention is.
Camera Techniques: Distance and Angle
Long shot (LS). Shot which shows all or most of a fairly large subject (for example, a
person) and usually much of the surroundings. Extreme Long Shot (ELS) - see
establishing shot: In this type of shot the camera is at its furthest distance from the
subject, emphasising the background. Medium Long Shot (MLS): In the case of a
standing actor, the lower frame line cuts off his feet and ankles. Some documentaries
with social themes favour keeping people in the longer shots, keeping social
circumstances rather than the individual as the focus of attention.
Establishing shot. Opening shot or sequence, frequently an exterior 'General View' as
an Extreme Long Shot (ELS). Used to set the scene.
Medium shots. Medium Shot or Mid-Shot (MS). In such a shot the subject or actor
and its setting occupy roughly equal areas in the frame. In the case of the standing
actor, the lower frame passes through the waist. There is space for hand gestures to be
seen. Medium Close Shot (MCS): The setting can still be seen. The lower frame line
passes through the chest of the actor. Medium shots are frequently used for the tight
presentation of two actors (the two shot), or with dexterity three (the three shot).
Close-up (CU). A picture which shows a fairly small part of the scene, such as a
character's face, in great detail so that it fills the screen. It abstracts the subject from a
context. MCU (Medium Close-Up): head and shoulders. BCU (Big Close-Up):
forehead to chin. Close-ups focus attention on a person's feelings or reactions, and are
sometimes used in interviews to show people in a state of emotional excitement, grief
or joy. In interviews, the use of BCUs may emphasise the interviewee's tension and
suggest lying or guilt. BCUs are rarely used for important public figures; MCUs are
preferred, the camera providing a sense of distance. Note that in western cultures the
space within about 24 inches (60 cm) is generally felt to be private space, and BCUs
may be invasive.
Angle of shot. The direction and height from which the camera takes the scene. The
convention is that in 'factual' programmes subjects should be shot from eye-level only.
In a high angle the camera looks down at a character, making the viewer feel more
powerful than him or her, or suggesting an air of detachment. A low angle shot places
camera below the character, exaggerating his or her importance. An overhead shot is
one made from a position directly above the action.
Viewpoint. The apparent distance and angle from which the camera views and records
the subject. Not to be confused with point-of-view shots or subjective camera shots.
Point-of-view shot (POV). A shot made from a camera position close to the line of
sight of a performer who is to be watching the action shown in the point-of-view shot.
Two-shot. A shot of two people together.
Selective focus. Rendering only part of the action field in sharp focus through the use
of a shallow depth of field. A shift of focus from foreground to background or vice
versa is called rack focus.
Soft focus. An effect in which the sharpness of an image, or part of it, is reduced by
the use of an optical device.
Wide-angle shot. A shot of a broad field of action taken with a wide-angle lens.
Tilted shot. When the camera is tilted on its axis so that normally vertical lines appear
slanted to the left or right, ordinary expectations are frustrated. Such shots are often
used in mystery and suspense films to create a sense of unease in the viewer.
Zoom. In zooming in the camera does not move; the lens is focussed down from a
long-shot to a close-up whilst the picture is still being shown. The subject is
magnified, and attention is concentrated on details previously invisible as the shot
tightens (contrast tracking). It may be used to surprise the viewer. Zooming out
reveals more of the scene (perhaps where a character is, or to whom he or she is
speaking) as the shot widens. Zooming in rapidly brings not only the subject but also
the background hurtling towards the viewer, which can be disconcerting. Zooming in
and then out creates an ugly 'yo-yo' effect.
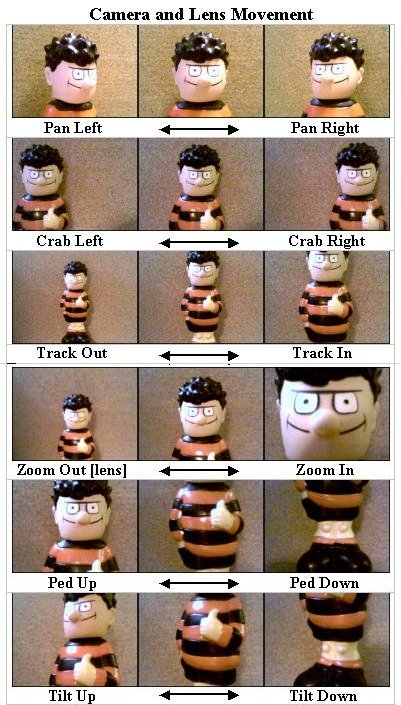
Following pan. The camera swivels (in the same base position) to follow a moving
subject. A space is left in front of the subject: the pan 'leads' rather than 'trails'. A pan
usually begins and ends with a few seconds of still picture to give greater impact. The
speed of a pan across a subject creates a particular mood as well as establishing the
viewer's relationship with the subject. 'Hosepiping' is continually panning across from
one person to another; it looks clumsy.
Surveying pan. The camera slowly searches the scene: may build to a climax or
anticlimax.
Tilt. A vertical movement of the camera - up or down- while the camera mounting
stays fixed.
Crab. The camera moves (crabs) right or left.
Tracking (dollying). Tracking involves the camera itself being moved smoothly
towards or away from the subject (contrast with zooming). Tracking in (like
zooming) draws the viewer into a closer, more intense relationship with the subject;
moving away tends to create emotional distance. Tracking back tends to divert
attention to the edges of the screen. The speed of tracking may affect the viewer's
mood. Rapid tracking (especially tracking in) is exciting; tracking back relaxes
interest. In a dramatic narrative we may sometimes be drawn forward towards a
subject against our will. Camera movement parallel to a moving subject permits speed
without drawing attention to the camera itself.
Hand-held camera. A hand-held camera can produce a jerky, bouncy, unsteady image
which may create a sense of immediacy or chaos. Its use is a form of subjective
treatment.
Process shot. A shot made of action in front of a rear projection screen having on it
still or moving images as a background.
There is always a reason for a cut, and you should ask yourself what the reason is.
Less abrupt transitions are achieved with the fade, dissolve, and wipe
Matched cut. In a 'matched cut' a familiar relationship between the shots may make
the change seem smooth:
*The cut is usually made on an action (for example, a person begins to turn towards a
door in one shot; the next shot, taken from the doorway, catches him completing the
turn). Because the viewer's eye is absorbed by the action he is unlikely to notice the
movement of the cut itself.
Jump cut. Abrupt switch from one scene to another which may be used deliberately to
make a dramatic point. Sometimes boldly used to begin or end action. Alternatively, it
may be result of poor pictorial continuity, perhaps from deleting a section.
Motivated cut. Cut made just at the point where what has occurred makes the viewer
immediately want to see something which is not currently visible (causing us, for
instance, to accept compression of time). A typical feature is the shot/reverse shot
technique (cuts coinciding with changes of speaker). Editing and camera work appear
to be determined by the action. It is intimately associated with the 'privileged point of
view' (see narrative style: objectivity).
Cutting rate. Frequent cuts may be used as deliberate interruptions to shock, surprise
or emphasize.
Cutting rhythm. A cutting rhythm may be progressively shortened to increase
tension. Cutting rhythm may create an exciting, lyrical or staccato effect in the viewer.
Cross-cut. A cut from one line of action to another. Also applied as an adjectuve to
sequences which use such cuts.
Cutaway/cutaway shot (CA). A bridging, intercut shot between two shots of the
same subject. It represents a secondary activity occurring at the same time as the main
action. It may be preceded by a definite look or glance out of frame by a participant, or
it may show something of which those in the preceding shot are unaware. (See
narrative style: parallel development) It may be used to avoid the technical ugliness
of a 'jump cut' where there would be uncomfortable jumps in time, place or viewpoint.
It is often used to shortcut the passing of time.
Reaction shot. Any shot, usually a cutaway, in which a participant reacts to action
which has just occurred.
Insert/insert shot. A bridging close-up shot inserted into the larger context, offering
an essential detail of the scene (or a reshooting of the action with a different shot size
or angle.)
Buffer shot (neutral shot). A bridging shot (normally taken with a separate camera)
to separate two shots which would have reversed the continuity of direction.
Fade, dissolve (mix). Both fades and dissolves are gradual transitions between shots.
In a fade the picture gradually appears from (fades in) or disappears to (fades out) a
blank screen. A slow fade-in is a quiet introduction to a scene; a slow fade-out is a
peaceful ending. Time lapses are often suggested by a slow fade-out and fade-in. A
dissolve (or mix) involves fading out one picture while fading up another on top of it.
The impression is of an image merging into and then becoming another. A slow mix
usually suggests differences in time and place. Defocus or ripple dissolves are
sometimes used to indicate flashbacks in time.
Superimpositions. Two of more images placed directly over each other (e.g. and eye
and a camera lens to create a visual metaphor).
Wipe. An optical effect marking a transition between two shots. It appears to supplant
an image by wiping it off the screen (as a line or in some complex pattern, such as by
appearing to turn a page). The wipe is a technique which draws attention to itself and
acts as a clear marker of change.
Inset. An inset is a special visual effect whereby a reduced shot is superimposed on the
main shot. Often used to reveal a close-up detail of the main shot.
Split screen. The division of the screen into parts which can show the viewer several
images at the same time (sometimes the same action from slightly different
perspectives, sometimes similar actions at different times). This can convey the
excitement and frenzy of certain activities, but it can also overload the viewer.
Stock shot. Footage already available and used for another purpose than the one for
which it was originally filmed.
Invisible editing: See narrative style: continuity editing.
Subjective time. The time experienced or felt by a character in a film, as revealed
through camera movement and editing (e.g. when a frightened person's flight from
danger is prolonged).
Compressed time. The compression of time between sequences or scenes, and within
scenes. This is the most frequent manipulation of time in films: it is achieved with cuts
or dissolves. In a dramatic narative, if climbing a staircase is not a significant part of
the plot, a shot of a character starting up the stairs may then cut to him entering a
room. The logic of the situation and our past experience of medium tells us that the
room is somewhere at the top of the stairs. Long journeys can be compressed into
seconds. Time may also be compressed between cutaways in parallel editing. More
subtle compression can occur after reaction shots or close-ups have intervened. The
use of dissolves was once a cue for the passage of a relatively long period of time.
Long take. A single shot (or take, or run of the camera) which lasts for a relatively
lengthy period of time. The long take has an 'authentic' feel since it is not inherently
dramatic.
Simultaneous time. Events in different places can be presented as occurring at the
same moment, by parallel editing or cross-cutting, by multiple images or split-screen.
The conventional clue to indicate that events or shots are taking place at the same time
is that there is no progression of shots: shots are either inserted into the main action or
alternated with each other until the strands are somehow united.
Slow motion. Action which takes place on the screen at a slower rate than the rate at
which the action took place before the camera. This is used: a) to make a fast action
visible; b) to make a familiar action strange; c) to emphasise a dramatic moment. It can
have a lyric and romantic quality or it can amplify violence.
Accelerated motion (undercranking) . This is used: a) to make a slow action visible;
b) to make a familiar action funny; c) to increase the thrill of speed.
Reverse motion. Reproducing action backwards, for comic, magical or explanatory
effect.
Replay. An action sequence repeated, often in slow motion, commonly featured in the
filming of sport to review a significant event.
Freeze-frame. This gives the image the appearance of a still photograph. Clearly not a
naturalistic device.
Flashback. A break in the chronology of a narrative in which events from the past are
disclosed to the viewer. Formerly indicated conventionally with defocus or ripple
dissolves.
Flashforward. Much less common than the flashback. Not normally associated with a
particular character. Associated with objective treatments.
Extended or expanded time/overlapping action. The expansion of time can be
accomplished by intercutting a series of shots, or by filming the action from different
angles and editing them together. Part of an action may be repeated from another
viewpoint, e.g. a character is shown from the inside of a building opening a door and
the next shot, from the outside, shows him opening it again. Used nakedly this device
disrupts the audience's sense of real time. The technique may be used unobtrusively to
stretch time, perhaps to exaggerate, for dramatic effect, the time taken to walk down a
corridor. Sometimes combined with slow motion.
Ambiguous time. Within the context of a well-defined time-scheme sequences may
occur which are ambiguous in time. This is most frequently comunicated through
dissolves and superimpositions.
Universal time. This is deliberately created to suggest universal relevance. Ideas
rather than examples are emphasised. Context may be disrupted by frequent cuts and
by the extensive use of close-ups and other shots which do not reveal a specific
background.
Studio sound. Sound recorded in the studio to improve the sound quality, eliminating
unwanted background noise ('ambient sound'), e.g. dubbed dialogue. This may be
then mixed with live environmental sound.
Selective sound. The removal of some sounds and the retention of others to make
significant sounds more recognizable, or for dramatic effect - to create atmosphere,
meaning and emotional nuance. Selective sound (and amplification) may make us
aware of a watch or a bomb ticking. This can sometimes be a subjective device,
leading us to identify with a character: to hear what he or she hears. Sound may be so
selective that the lack of ambient sound can make it seem artificial or expressionistic.
Sound perspective/aural perspective. The impression of distance in sound, usually
created through the use of selective sound. Note that even in live television a
microphone is deliberately positioned, just as the camera is, and therefore may
privilege certain participants.
Sound bridge. Adding to continuity through sound, by running sound (narration,
dialogue or music) from one shot across a cut to another shot to make the action seem
uninterrupted.
Dubbed dialogue. Post-recording the voice-track in the studio, the actors matching
their words to the on-screen lip movements. Not confined to foreign-language
dubbing.
Wildtrack (asynchronous sound). Sound which was self-evidently recorded
separately from the visuals with which it is shown. For example, a studio voice-over
added to a visual sequence later.
Parallel (synchronous) sound. Sound 'caused' by some event on screen, and which
matches the action.
Commentary/voice-over narration. Commentary spoken off-screen over the shots
shown. The voice-over can be used to:
The commentary confers authority on a particular interpretation, particularly if the tone
is moderate, assured and reasoned. In dramatic films, it may be the voice of one of the
characters, unheard by the others.
Sound effects (SFX). Any sound from any source other than synchronised dialogue,
narration or music. Dubbed-in sound effects can add to the illusion of reality: a stage-
set door may gain from the addition of the sound of a heavy door slamming or
creaking.
Music. Music helps to establish a sense of the pace of the accompanying scene. The
rhythm of music usually dictates the rhythm of the cuts. The emotional colouring of the
music also reinforces the mood of the scene. Background music is asynchronous
music which accompanies a film. It is not normally intended to be noticeable.
Conventionally, background music accelerates for a chase sequence, becomes louder
to underscore a dramatically important action. Through repetition it can also link shots,
scenes and sequences. Foreground music is often synchronous music which finds its
source within the screen events (e.g. from a radio, TV, stereo or musicians in the
scene). It may be a more credible and dramatically plausible way of bringing music into
a programme than background music (a string orchestra sometimes seems bizarre in a
Western).
Silence. The juxtaposition of an image and silence can frustrate expectations, provoke
odd, self-conscious responses, intensify our attention, make us apprehensive, or make
us feel dissociated from reality.
Backlighting. A romantic heroine is often backlit to create a halo effect on her hair.
Graphics. Maps, graphs and diagrams are associated primarily with news,
documentary and educational programmes.
Animation. Creating an illusion of movement, by inter-cutting stills, using graphics
with movable sections, using step-by-step changes, or control wire activation.
Objective treatment. The 'objective point of view' involves treating the viewer as an
observer. A major example is the 'privileged point of view' which involves watching
from omniscient vantage points. Keeping the camera still whilst the subject moves
towards or away from it is an objective camera effect.
Parallel development/parallel editing/cross-cutting. An intercut sequence of shots
in which the camera shifts back and forth between one scene and another. Two distinct
but related events seem to be happening at approximately the same time. A chase is a
good example. Each scene serves as a cutaway for the other. Adds tension and
excitement to dramatic action.
'Invisible editing'. This is the omniscient style of the realist feature films developed in
Hollywood. The vast majority of narrative films are now edited in this way. The cuts
are intended to be unobtrusive except for special dramatic shots. It supports rather
than dominates the narrative: the story and the behaviour of its characters are the
centre of attention. The technique gives the impression that the edits are always
required are motivated by the events in the 'reality' that the camera is recording rather
than the result of a desire to tell a story in a particular way. The 'seamlessness'
convinces us of its 'realism', but its devices include:
The editing isn't really 'invisible', but the conventions have become so familiar to visual
literates that they no longer consciously notice them.
Mise-en-scene. (Contrast montage). 'Realistic' technique whereby meaning is
conveyed through the relationship of things visible within a single shot (rather than, as
with montage, the relationship between shots). An attempt is preserve space and time
as much as possible; editing or fragmenting of scenes is minimised. Composition is
therefore extremely important. The way people stand and move in relation to each
other is important. Long shots and long takes are characteristic.
Montage/montage editing. In its broadest meaning, the process of cutting up film and
editing it into the screened sequence. However, it may also be used to mean intellectual
montage - the juxstaposition of short shots to represent action or ideas - or (especially
in Hollywood), simply cutting between shots to condense a series of events.
Intellectual montage is used to consciously convey subjective messages through the
juxtaposition of shots which are related in composition or movement, through
repetition of images, through cutting rhythm, detail or metaphor. Montage editing,
unlike invisible editing, uses conspicuous techniques which may include: use of close-
ups, relatively frequent cuts, dissolves, superimposition, fades and jump cuts. Such
editing should suggest a particular meaning.
Talk to camera. The sight of a person looking ('full face') and talking directly at the
camera establishes their authority or 'expert' status with the audience. Only certain
people are normally allowed to do this, such as announcers, presenters, newsreaders,
weather forecasters, interviewers, anchor-persons, and, on special occasions (e.g.
ministerial broadcasts), key public figures. The words of 'ordinary' people are normally
mediated by an interviewer. In a play or film talking to camera clearly breaks out of
naturalistic conventions (the speaker may seem like an obtrusive narrator). A short
sequence of this kind in a 'factual' programme is called a 'piece to camera'.
Tone. The mood or atmosphere of a programme (e.g. ironic, comic, nostalgic,
romantic).
Scene. A dramatic unit composed of a single or several shots. A scene usually takes
place in a continuous time period, in the same setting, and involves the same
characters.
Sequence. A dramatic unit composed of several scenes, all linked together by their
emotional and narrative momentum.
Genre. Broad category of television or film programme. Genres include: soap operas,
documentaries, game shows, 'cop shows' (police dramas), news programmes, 'chat'
shows, phone-ins and sitcoms (situation comedies).
Series. A succession of programmes with a standard format.
Serial. An ongoing story in which each episode takes up where the last one left off.
Soap operas are serials.
Talking heads. In some science programmes extensive use is made of interviews with
a succession of specialists/ experts (the interviewer's questions having been edited out).
This derogatively referred to as 'talking heads'. Speakers are sometimes allowed to talk
to camera. The various interviews are sometimes cut together as if it were a debate,
although the speakers are rarely in direct conversation.
Vox pop. Short for 'vox populi', Latin for 'voice of the people'. The same question is
put to a range of people to give a flavour of 'what ordinary people think' about some
issue. Answers are selected and edited together to achieve a rapid-fire stream of
opinions.
Intertextuality. Intertextuality refers to relationships between different elements of a
medium (e.g. formats and participants), and links with other media. One aspect of
intertextuality is that programme participants who are known to the audience from
other programmes bring with them images established in other contexts which effect
the audience's perception of their current role. Another concerns issues arising from
sandwiching advertisements between programmes on commercial television (young
children, in particular, may make no clear distinction between them).
Daniel Chandler
This page has been accessed
times since 18th September 1995.

Images and text (c) 2001 Daniel Chandler - no unauthorized use -
this image is watermarked

Images and text (c) 2001 Daniel Chandler - no unauthorized use -
this image is watermarked
Camera Techniques: Movement

Images and text (c) 2001 Daniel Chandler - no unauthorized use -
this image is watermarked
Editing Techniques
Cut. Sudden change of shot from one viewpoint or location to another. On television
cuts occur on average about every 7 or 8 seconds. Cutting may:
Manipulating Time
Screen time: a period of time represented by events within a film (e.g. a day, a week). Use of Sound
Direct sound. Live sound. This may have a sense of freshness, spontaneity and
'authentic' atmosphere, but it may not be acoustically ideal.
Lighting
Soft and harsh lighting. Soft and harsh lighting can manipulate a viewer's attitude
towards a setting or a character. The way light is used can make objects, people and
environments look beautiful or ugly, soft or harsh, artificial or real. Light may be used
expressively or realitically. Graphics
Text. Titles appear at or near the start of the programme. Their style - typeface, size,
colour, background and pace - (together with music) can establish expectations about
the atmosphere and style of the programme. Credits listing the main actors, the
director, and so on, are normally shown at or near the beginning, whilst those listing
the rest of the actors and programme makers are normally shown at the end. Some
American narrative series begin with a lengthy pre-credit sequence. Credits are
frequently superimposed on action or stills, and may be shown as a sequence of frames
or scrolled up the screen. Captions are commonly used in news and documentaries to
identify speakers, in documentaries, documentary dramas and dramatic naratives to
indicate dates or locations. Subtitles at the bottom of the screen are usually used for
translation or for the benefit of the hearing-impaired. Narrative style
Subjective treatment. The camera treatment is called 'subjective' when the viewer is
treated as a participant (e.g. when the camera is addressed directly or when it imitates
the viewpoint or movement of a character). We may be shown not only what a
character sees, but how he or she sees it. A temporary 'first-person' use of camera as
the character can be effective in conveying unusual states of mind or powerful
experiences, such as dreaming, remembering, or moving very fast. If overused, it can
draw too much attention to the camera. Moving the camera (or zooming) is a
subjective camera effect, especially if the movement is not gradual or smooth.
Formats and other features
Shot. A single run of the camera or the piece of film resulting from such a run. Further Reading
UWA 1994