Return to Lab 01
Return to Lab 06
Return to Slide List
Granuloma - Ghon Tubercle (PH 1225) (pp. 50-52, Fig
4-13)
(Be
able to identify this slide at 40X or 100X, identify the tubercle capsule and the necrotic area; and
differentiate between the normal and abnormal regions.)
Notice that an area of lung tissue has been displaced by a dense spherical
mass of necrosis surrounded by a capsule of fibrous connective tissue.
Normal lung
(40X2.0)
Normal lung (100X2.0)
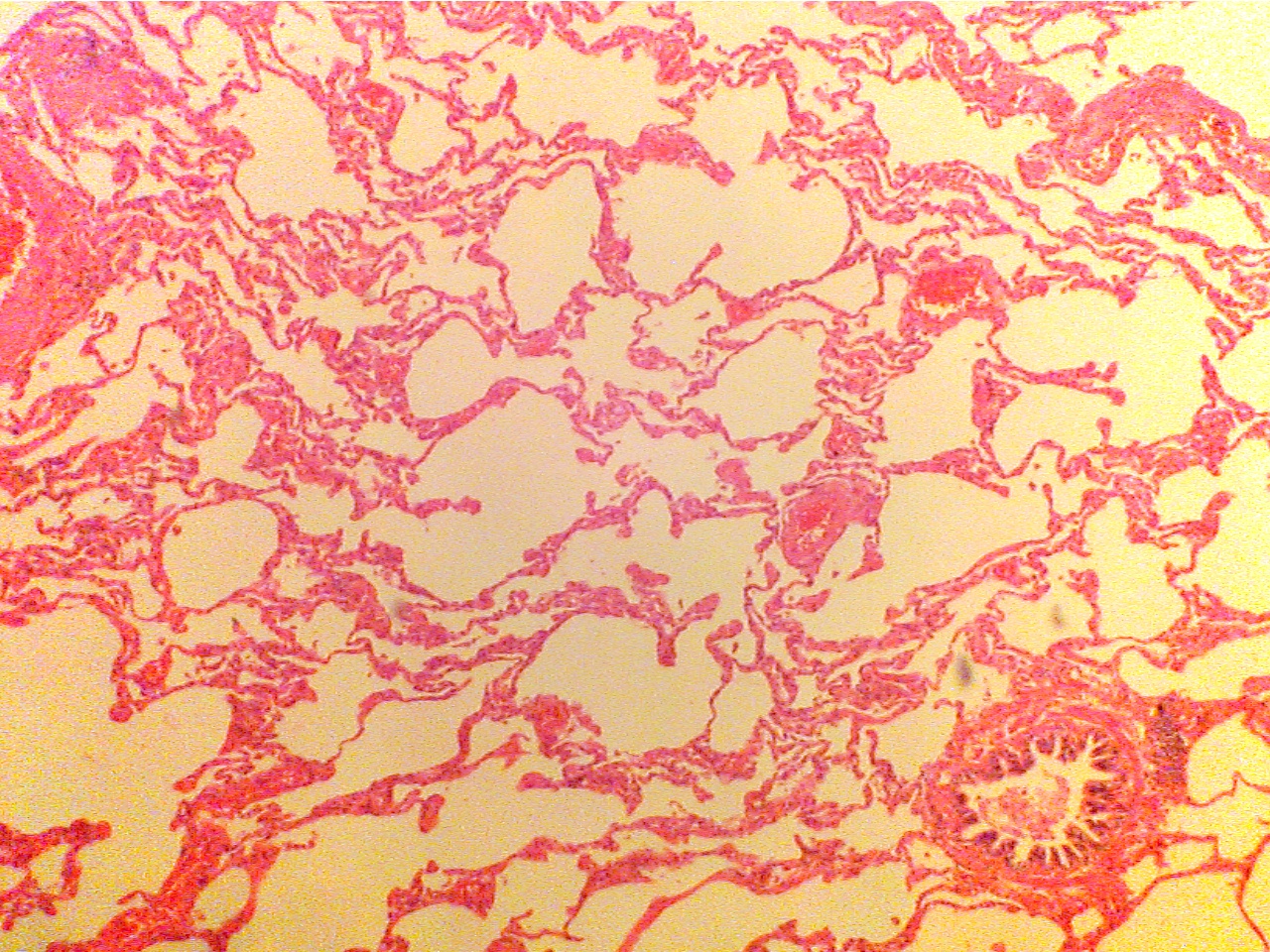
Much normal tissue creates large surface
area
Much normal tissue creates large surface area
with many capillaries, many small air spaces. Large
with many capillaries, which are filled with
vessel at extreme left, large airway at lower right
RBCs (red cells)
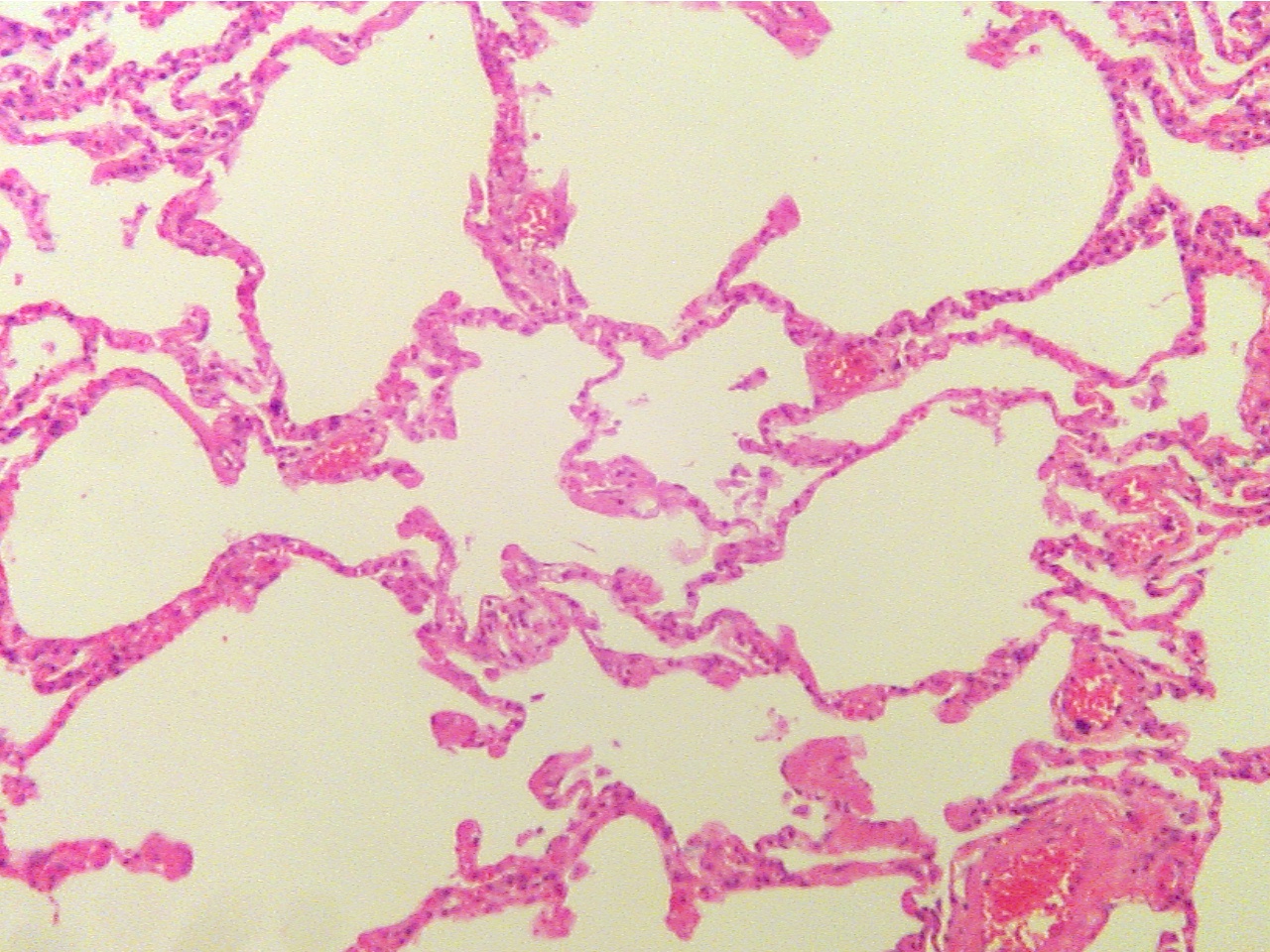
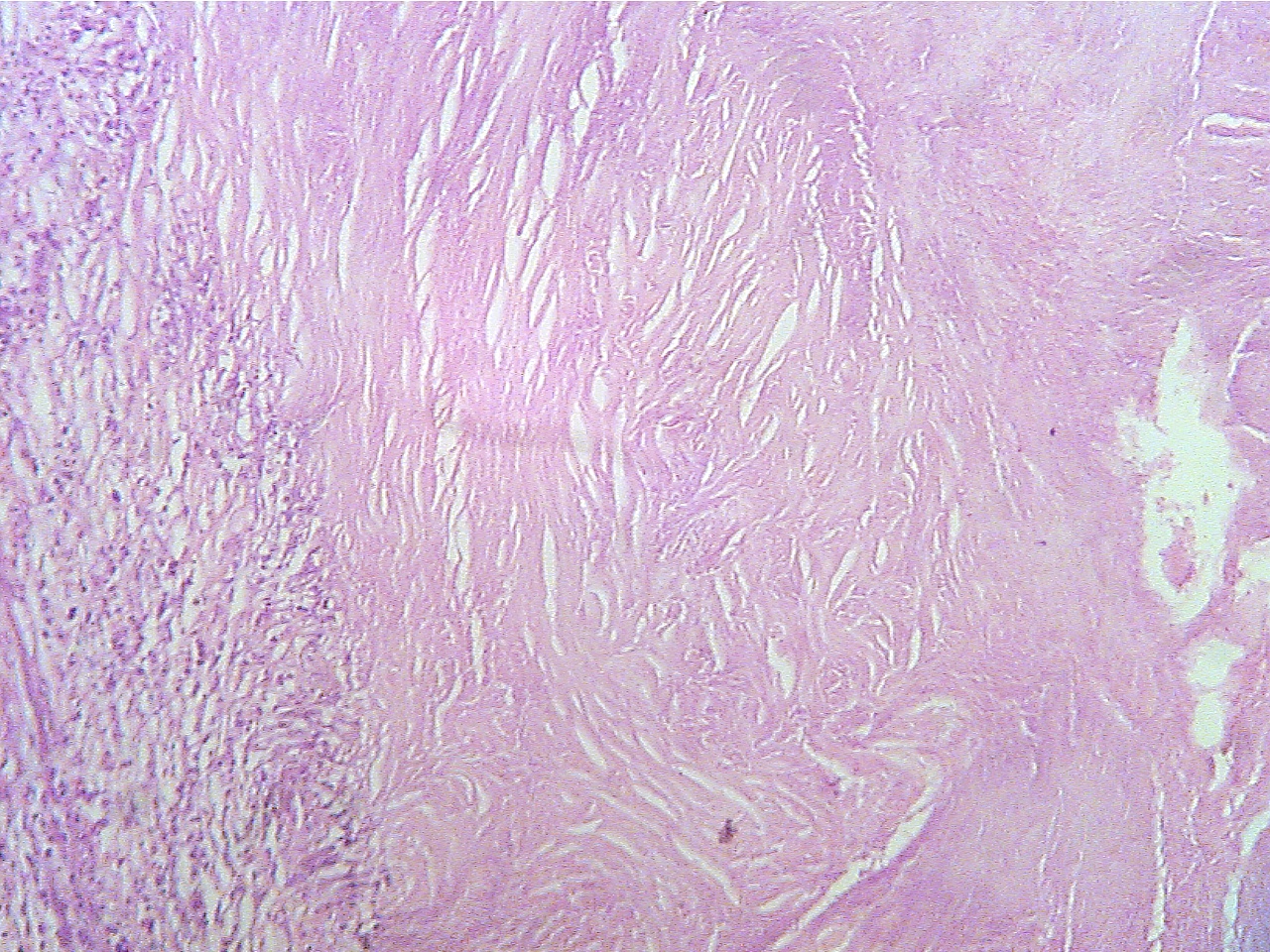
Ghon tubercle - entire (40X1.0)
Ghon tubercle (40X2.0)
Tubercle in center with necrotic core surrounded
by Normal lung (lower
left), capsule (granular and fibrous
capsule, normal lung on extreme left and
right
layers), and core of necrotic material
(center to right edge)
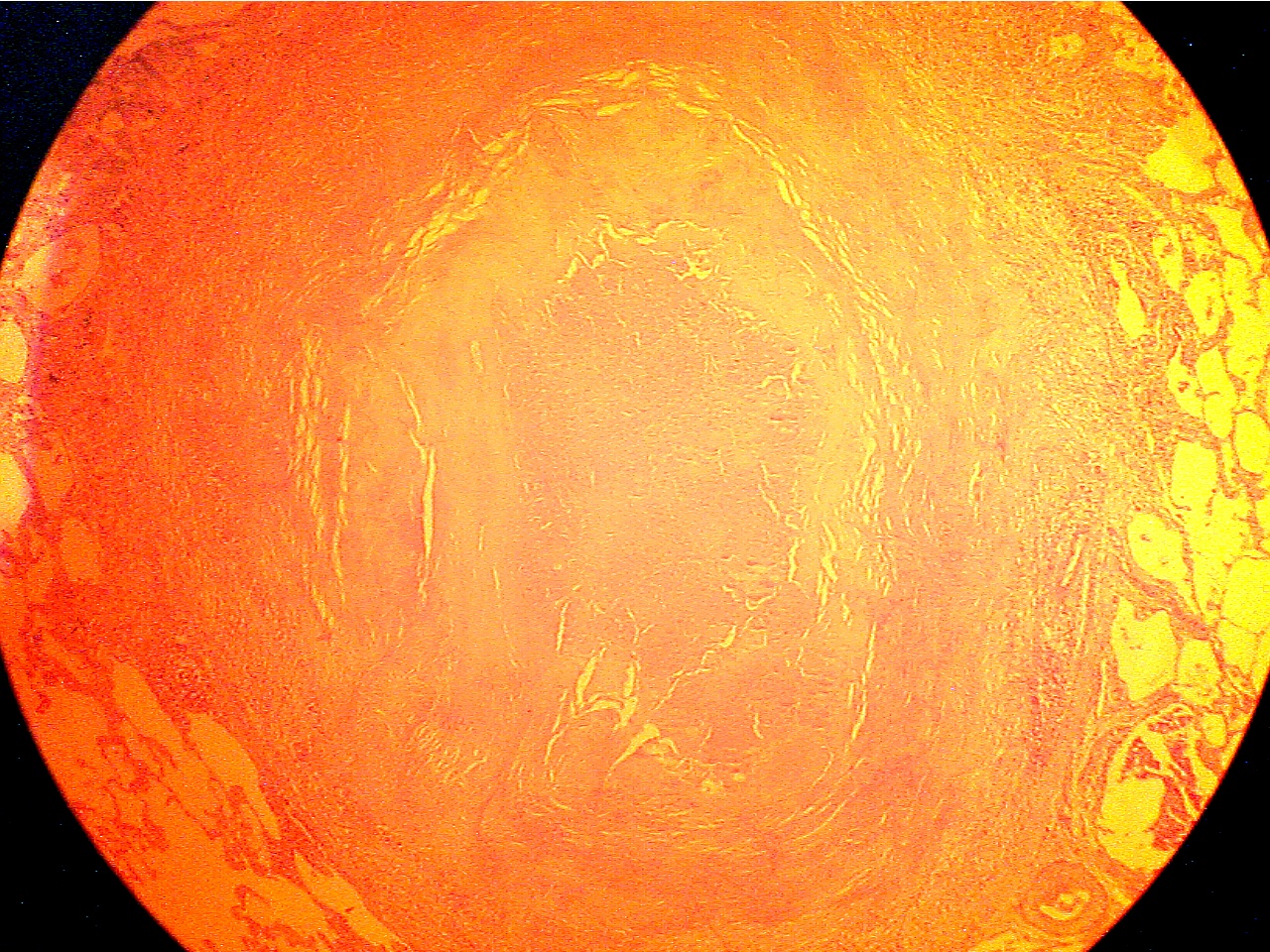
Ghon
tubercle (100X1.6)
Ghon tubercle (400X2.0)
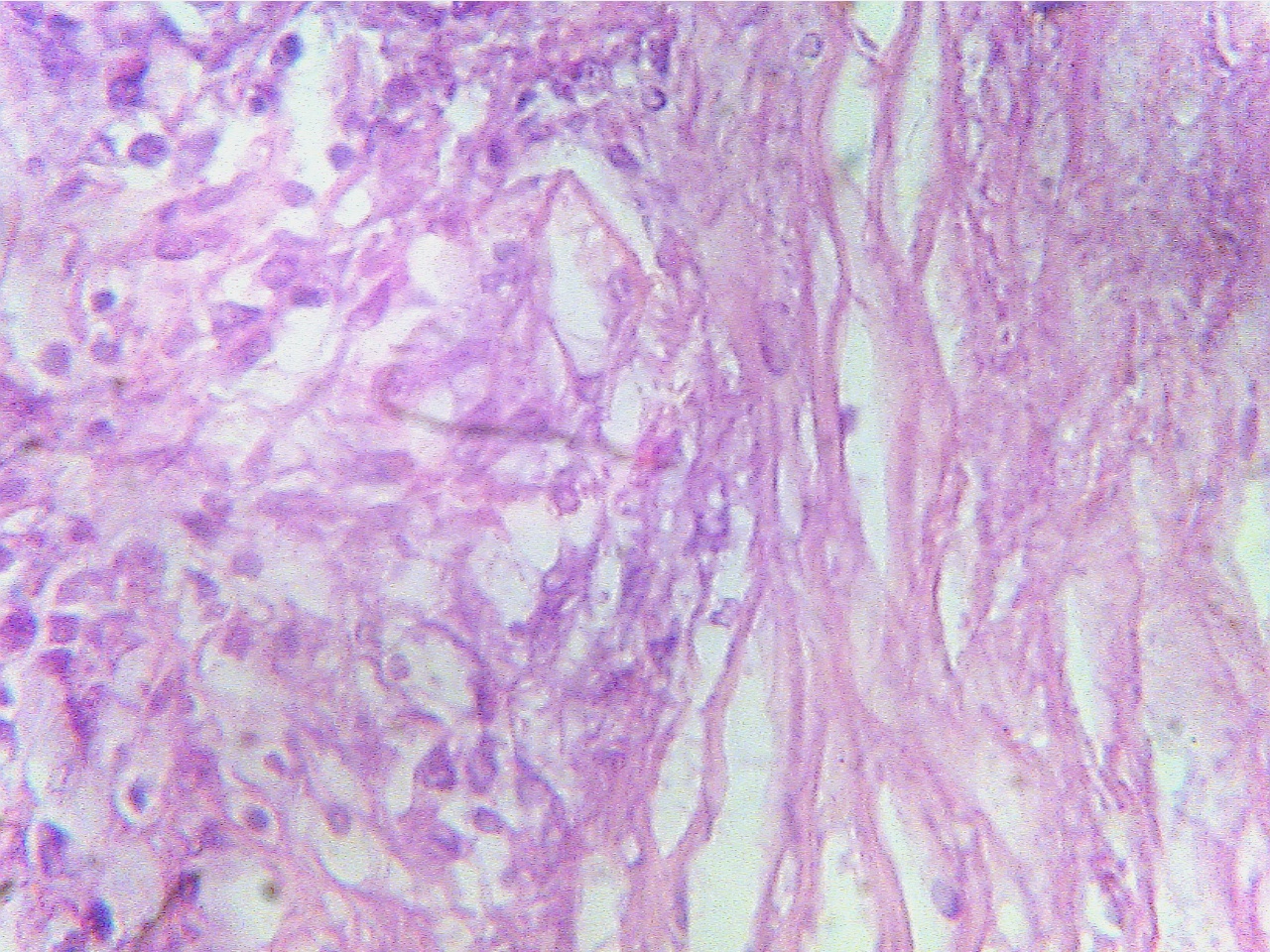
Macrophages (left), fibrous capsule
(center), necrotic Macrophages
(round dark blue at left), fibrous capsule
region
(right)
(right)
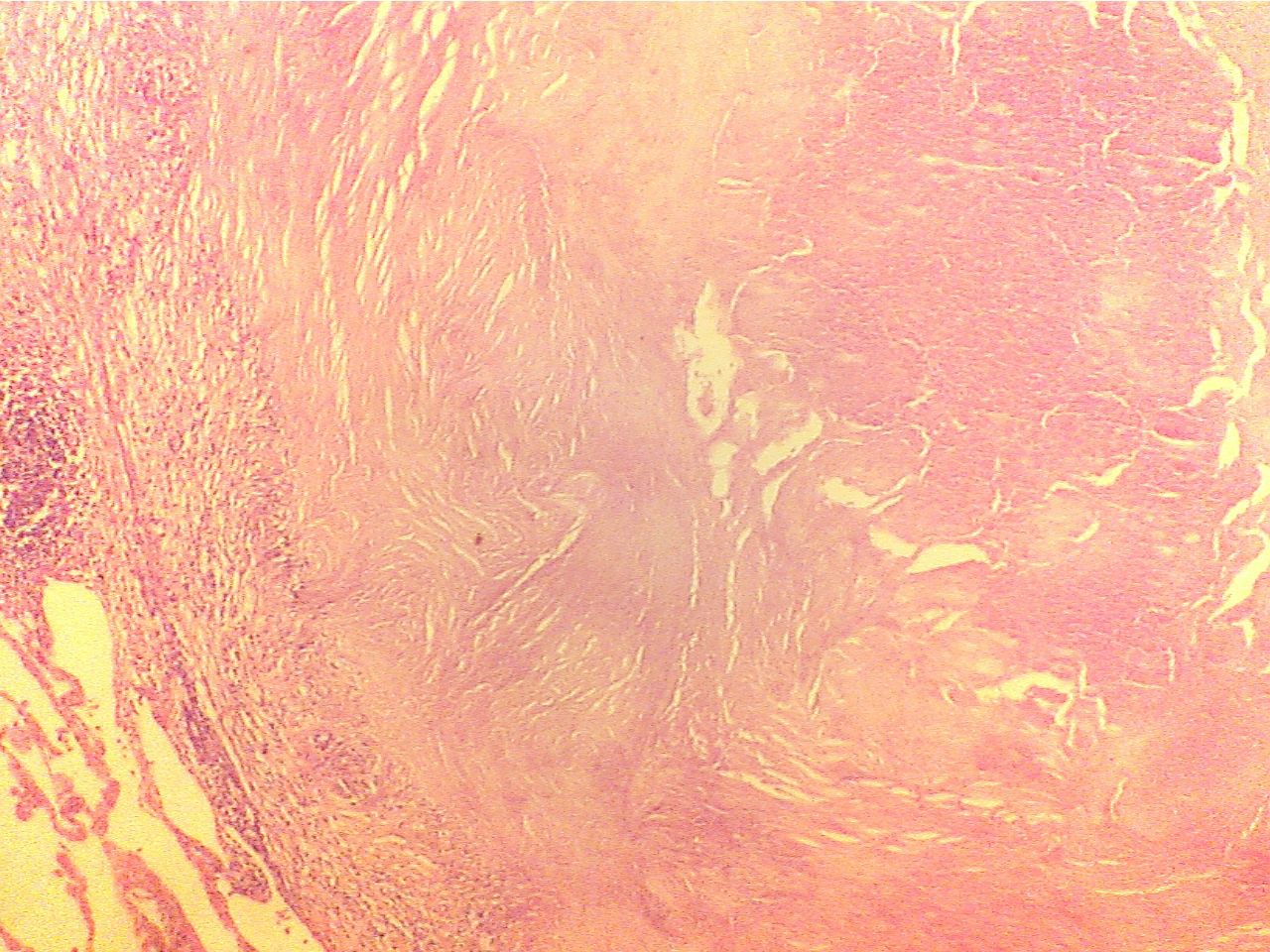
Ghon tubercle (400X2.8)
Ghon
tubercle (400X2.8)
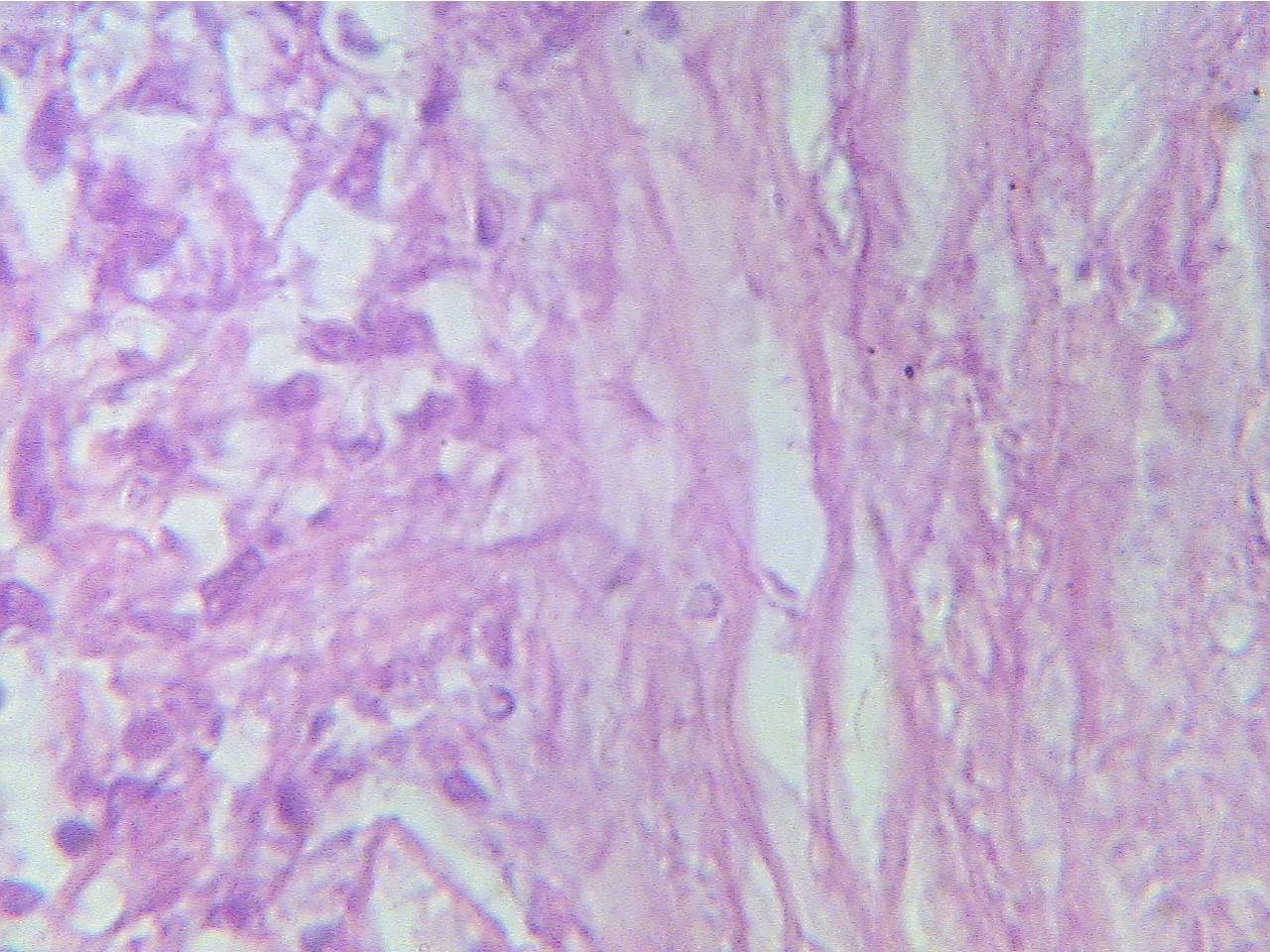
Macrophages (round dark blue at left), fibrous
capsule Central amorphous
acellular necrotic region
(right)
* What type of necrosis is present in this lesion?
Compare the dense arrangement of material in the granuloma with the open,
air-filled normal lung tissue surrounding it by moving the slide from one area
to another.
* What effect does this lesion have on gas exchange in this area?
* With what disease are Ghon tubercles associated?
Observe the granuloma with both the compound and dissecting scopes and then
return the slide to the original position.
Return to Lab 01
Return to Lab 06
Return to Slide List
8Copyright
2001 - Augustine G. DiGiovanna - All rights reserved.
This
material may not be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or
stored in any data base or retrieval system without prior written permission is
obtained from Augustine G. DiGiovanna, Ph.D., Professor of Biology,
Salisbury University, Salisbury, MD 21801.







