|
Chapter 22 Lecture Notes
 Formulas: Formulas:
SBúúDl = moI + moeoDFE/Dt
FE = EA
l = c/f
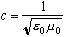
S = P/A = U/tA =uV /tA = uc
u = U/V = (1/2)eoE2 + 1/(2mo)B2 =eoE2 = (1/mo)B2
 Demonstrations: Demonstrations:
- Show a transverse wave (rope), and a longitudinal wave (slinky).
- Energy of a short wave transmitter
- EM spectrum
Electromagnetic Waves
Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields
 We have learned in Chapter 21 that changing magnetic fields
create electric fields. In the mid-1800's, the famous Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwellhypothesized that changing electric fields might also
create magnetic fields and that this interaction would create electromagnetic (EM) waves, waves of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. He predicted that
the speed of these electromagnetic waves would be the speed of light. Consequently, he predicted that visible light was an electromagnetic wave.
Let's look at the first part of his theory, that changing electric fields produce magnetic fields. We have learned in Chapter 21 that changing magnetic fields
create electric fields. In the mid-1800's, the famous Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwellhypothesized that changing electric fields might also
create magnetic fields and that this interaction would create electromagnetic (EM) waves, waves of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. He predicted that
the speed of these electromagnetic waves would be the speed of light. Consequently, he predicted that visible light was an electromagnetic wave.
Let's look at the first part of his theory, that changing electric fields produce magnetic fields.
Your book describes how Maxwell hypothesized something called the displacement current
, which was shown to be equivalent to a changing electric flux. That is
ID= eoDFE/Dt
where the electric flux (FE) is defined in the same way as the magnetic flux, the amount of electric
field going through an area.
FE = EA
Maxwell showed that with this definition, Ampere's Law had an additional term and should be written.
SBúúDl = moI + moeoDFE/Dt
Recall that Ampere's Law stated in mathematical terms that a current produced a
magnetic field. With this additional term, Maxwell showed that a changing electric flux would create a magnetic field, as well. So now we have the ideas that a changing electric
flux creates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic flux creates an electric field. Maxwell realized that this would lead to the production and self-propagation of electromagnetic waves. Let's see how this works.
Production of EM Waves
Let's assume we have an antenna, which is just some kind of wire that is connected to
an ac source. The ac source produces oscillating + and - charges which set up electric field (due to the separation of charge) and a magnetic field (due to the current in the wire).
Note that the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. This field begins to move
away from the antenna and in a little while the ac source has caused the situation to reverse.
We have a magnetic field that is oscillating in and out of the paper and an electric field
that is oscillating up and down in the paper. Since a changing magnetic field creates an electric field and a changing electric field creates a magnetic field, these two oscillating
fields continue to reinforce each other, and the wave propagates through space.
We have shown how to create an EM waves using an antenna. In general, electromagnetic waves are created by any accelerating charge.
The Nature of EM Waves
What are the properties of these electromagnetic waves?
Transverse Wave
Demonstration: Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
They are transverse waves. That means the direction of oscillation is perpendicular to
the direction of motion. The electric and magnetic fields are sinusoidally oscillating perpendicular to the direction of motion.
Composed of Electric and Magnetic Fields
The waves are composed of electric and magnetic fields. As we have seen,
- The fields are oscillating
- The fields are at right angles to each other
- The fields are at right angles to direction of motion
- The fields are in phase. The peak of the magnetic field occurs at the same time as the peak of the electric field.
The Speed of EM Waves
One amazing thing about Maxwell's hypothesis was that he predicted what the speed of
electromagnetic radiation should be. The book shows briefly how to calculate this from principles that we already know. Using a similar method, Maxwell showed that the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum would be
c =(eomo)-1/2
c = 1/[(8.85´10-12C2/(N-m2)(4p´10-7T-m/A)]1/2
c = 3.00´108 m/s2
We check that the units are okay.
F = ILBÞ N = C×m×T/s T = N×s/C×m
Amps = C/s, so the units above are
{(N×m2/C2)(C×m/N×s)(1/m)(C/s)}1/2 = {m2/s2}1/2 = m/s
This is amazing. He predicted that the speed of light would be exactly what we measure
it to be. Galileo had tried to measure the speed of light using lanterns and an assistant at a distant location. A more accurate way of measuring the speed of light is using a rotating mirror.
The eight-sided mirror rotates, and the eye can only see the light from the box when the
mirror rotates exactly 1/8 of a revolution in the time it takes the light to bounce off the mirror and come back. Since the time it takes to make one rotation is given by the period, T = 1/f = 2p/w, one eighth of a rotation takes a time of t =p/4w,
Or v = d/t = 4dw/p
So by knowing the angular rotation (w) and the distance (d) precisely, one can measure the speed
of light precisely.
The speed of light is FAST. It is 3.00´108 m/s2 or 186,000 miles/second.
The Spectrum of EM Waves
Electromagnetic waves come in a variety of wavelengths that appear very different to
our senses or detectors, but are all electromagnetic waves. These include: radio waves (AM, FM), television signals, microwaves, infrared waves (heat), visible light, ultraviolet rays
(cause skin cancer), x-rays, gamma rays. Because these are all electromagnetic waves,
- They have the same speed.
- They have different frequency and wavelength.
The velocity of a wave is given by
v = c = lf.
So if I know the frequency, I can determine the wavelength, and vice versa.
Demonstration: The em spectrum.
I show one characteristic frequency, when really everything is a range.
|
Name
|
Frequency
|
Wavelength (l)
|
Time for one l
|
|
Extra Low Freq
|
60 Hz
|
5000 km (5´106)
|
17 ms (1.7´10-2)
|
|
Audio Frequency
|
10 kHz (1´104)
|
30 km (3´104)
|
100 ms (1´10-4)
|
|
Radio Frequency
|
222 MHz (2´108)
|
1.4 m
|
4.5 ns (4.5´10-9)
|
|
Microwave
|
10 GHz (1´1010)
|
30 mm (3´10-2)
|
100 ps (1´10-10)
|
|
Infrared (Heat)
|
10 THz (1´1013)
|
30 mm (3´10-5)
|
100 fs (1´10-13)
|
|
Visible
|
600 Thz (6´1014)
|
500 nm (5´10-7)
|
1.7 fs (1.7´10-15)
|
|
Ultraviolet
|
1´1016 Hz
|
30 nm (3´10-8)
|
.1 fs (1´10-16)
|
|
X-ray
|
1´1018 Hz
|
300 pm (3´10-10)
|
1´10-18 s
|
|
Gamma-ray
|
1´1020 Hz
|
3 pm (3´10-12)
|
1´10-20 s
|
|
The Energy of EM Waves
We have seen in our study of electricity and magnetism that there is energy stored in a
magnetic field and in an electric field. They have energy densities.
ue = (1/2)eoE2
um = (1/2mo)B2
Because em waves are oscillating electric and magnetic fields, they, too carry energy. In
an em wave, the total energy density is just the sum of the contributions from the electric and magnetic waves.
u = (1/2)eoE2 + (1/2mo)B2
The energy carried in the magnetic field is the same as the energy in the electric field.
(1/2)eoE2 = (1/2mo)B2 so E = cB
So we can write density as u = eoE2 or u = (1/mo)B2
As always with sinusoidal waves
ERMS = (1/Ö2)Eo and BRMS = (1/Ö2)Bo
We often measure the energy stored in an em wave by measuring its intensity, which is
the total power that passes through a unit area. (This heat is intense. Your body is the area). (S is the intensity)
S = P/A = U/tA measured in watts/m2
S = uV/tA (V is volume = Al = Avt = Act)
S = uAct/tA = uc
S = (1/2)ceoE2 + (c/2mo)B2 or S = ceoE2 or S = (c/mo)B2
Demonstration: Show power transferred in short wave radio and with heating element.
 |
 |
|
 PROBLEM
: A light bulb has an RMS power output of 100 watts. If I
am standing 2 meters from the bulb, how much energy do I feel on my face in one minute if my face has an area of 0.02 m2? PROBLEM
: A light bulb has an RMS power output of 100 watts. If I
am standing 2 meters from the bulb, how much energy do I feel on my face in one minute if my face has an area of 0.02 m2?
When the light has gone a distance of 2 meters from the bulb,
the 100 watts has spread out into a cross sectional area given by the 4pr2 = 4p(2m)2 = 50.3m2.
The average power per unit area is then given by
S = P/A =100 W/(50.3 m)2 = 2.0 W/m2
and the average power reaching my face is
P = SA = (2.0 W/m2)(0.02 m2) = .040 W
U = Pt = (0.40 W)(60 s) = 2.4 Joules
What is the rms magnetic field incident on my face?
S = (c/mo)B2
B = (moS/c)1/2 = {(4p´10-7 T×m/A)(2.0 W/m2)/(3.00´108 m/s)}1/2
B = 9.2´10-8 T
Check the units:
(T×m×W×s/A×m3) 1/2 = (T×m×s×{(N×m)/s}/A×m3) 1/2 = (T×N/A×m) 1/2 = (T2) 1/2 = T
|
|
|
|